The Partnership for a Drug Free America – This web site provides “provides advice and stories from parents and professionals about drug prevention, intervention and raising healthy teens.”
https://alcoholicsanonymous.com/aa-meetings/indiana/ – Discover Indiana Alcoholics Anonymous meetings per county or city, and take the next step to overcome alcohol addiction.
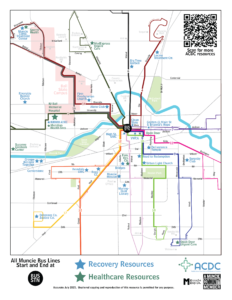
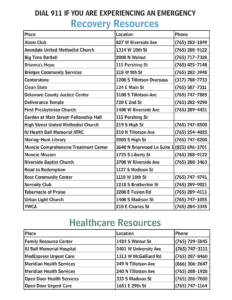
Community Anti Drug Coalitions of America: This web site provides a variety of resources on drugs and alcohol as well as information on community coalitions.
National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA): part of the of the National Institute on Health, a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIDA’s mission is to “to lead the Nation in bringing the power of science to bear on drug abuse and addiction.”
National Institute on Health: NIH is the primary federal agency for conducting and supporting medical research.
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: “The Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) is the United States government’s principal agency for protecting the health of all Americans and providing essential human services, especially for those who are least able to help themselves.”
Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration: SAMHSA’s mission “is to reduce the impact of substance abuse and mental illness on America’s communities.”
Office of National Drug Control Policy: “The principal purpose of ONDCP is to establish policies, priorities, and objectives for the Nation’s drug control program.”
Indiana Division of Mental Health and Addition: this agency is responsible for insuring that Indiana residents have “access to appropriate mental health and addiction services that promote an individuals self sufficiency.”
Family and Social Services Administration: this agency is responsible for the administration of family/children assistance, and adult and child protection.
Center for Disease Control and Prevention: provides health information on substance abuse and other topics.
Indiana Criminal Justice Institute.